Finding relief from tennis elbow
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is a common and often painful condition that affects the outer part of the elbow. Despite its name, you don’t have to be a tennis player to develop this condition; it can occur in anyone who repeatedly uses their forearm muscles and tendons, leading to overuse and strain.
It’s a bit like your elbow’s way of saying, “Hey, I need a break!” So, if you’re experiencing persistent pain and tenderness in that area, it might be time to seek some relief and figure out what your elbow is trying to tell you.
What is tennis elbow?
Tennis elbow is a form of tendinitis, characterised by the inflammation or degeneration of the tendons on the outer part of the elbow. The condition typically arises from repetitive motions and overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons.
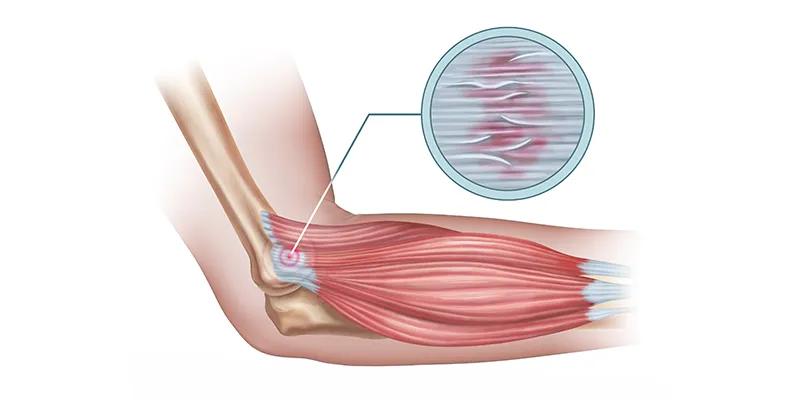
Causes
- Overuse and repetitive strain: The primary cause of tennis elbow is overuse and repetitive strain on the forearm muscles and tendons. Engaging in activities that involve constant gripping, twisting or extending the wrist and fingers can lead to micro-tears in the tendons, resulting in inflammation and pain.
- Sports activities: While tennis is a notable contributor, other sports and activities can also lead to tennis elbow. These include racquet sports, golf, heavy weightlifting and any activity that involves repetitive arm movements.
- Occupational factors: Certain occupations pose a higher risk of developing tennis elbow due to repetitive hand and wrist movements. Jobs such as plumbing, carpentry, painting and typing can contribute to the condition over time.

- Age and gender: Tennis elbow is more common in individuals between the ages of 30 and 50. Additionally, it affects both men and women, although men may be slightly more prone to developing this condition.
- Improper technique: Incorrect technique during sports or manual labor can significantly increase the risk of tennis elbow. Using poor form while executing repetitive movements puts excessive stress on the tendons, making them more susceptible to injury.
- Lack of warm-up: Insufficient warm-up before engaging in physical activities can contribute to the development of tennis elbow. Cold muscles and tendons are more prone to strain and injury, emphasising the importance of proper warm-up exercises.
- Poor equipment: Using sports equipment that is not suited to your size, strength or playing style can contribute to tennis elbow. For example, using a tennis racquet with a grip that is too small or too large may increase the risk.
- Genetics and health factors: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to conditions like tennis elbow. Additionally, certain health factors, such as obesity and inflammatory conditions, can contribute to an increased likelihood of developing this condition.
Symptoms
- Pain on the outer side of the elbow: The primary symptom of tennis elbow is pain or tenderness on the outer part of the elbow. This area corresponds to the lateral epicondyle, the bony bump where the forearm muscles attach.
- Pain that radiates down the forearm: The pain associated with tennis elbow may extend from the outer elbow down the forearm. It often follows the path of the forearm muscles.
- Grip weakness: Individuals with tennis elbow may experience weakness in their grip. This can make it challenging to perform simple tasks such as holding a cup or shaking hands.
- Pain exacerbated by gripping or lifting: Activities that involve gripping or lifting objects, especially with the palm facing downward, can intensify the pain. This includes actions like lifting a suitcase, carrying groceries or even holding a racquet for sports.
- Stiffness in the elbow: Stiffness may accompany tennis elbow, making it difficult to fully bend or straighten the arm. This stiffness can contribute to discomfort and limited range of motion.
- Worsening pain with repetitive movements: The pain tends to worsen with repetitive movements of the forearm, such as typing, using a mouse or performing activities that involve repetitive wrist extension.
- Pain during activities involving wrist movement: Engaging in activities that require repetitive wrist movement, like playing tennis, gripping tools or turning a screwdriver, can trigger or exacerbate the pain.
- Morning stiffness and discomfort: Some individuals may experience stiffness and discomfort in the elbow, particularly in the morning. This stiffness can gradually improve as the day progresses.
- Tenderness to touch: The outer part of the elbow may be tender to touch. Applying pressure to the affected area can elicit pain and discomfort.
- Difficulty holding small objects: People with tennis elbow may find it challenging to hold or grasp small objects, and they may feel increased discomfort when trying to perform tasks that involve fine motor skills.

Treatments
- Rest and modification of activities: Giving the affected arm adequate rest is crucial. Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, especially those involving repetitive wrist and forearm movements, allows the injured tendons to heal. Modifications in work or sports activities may be necessary.
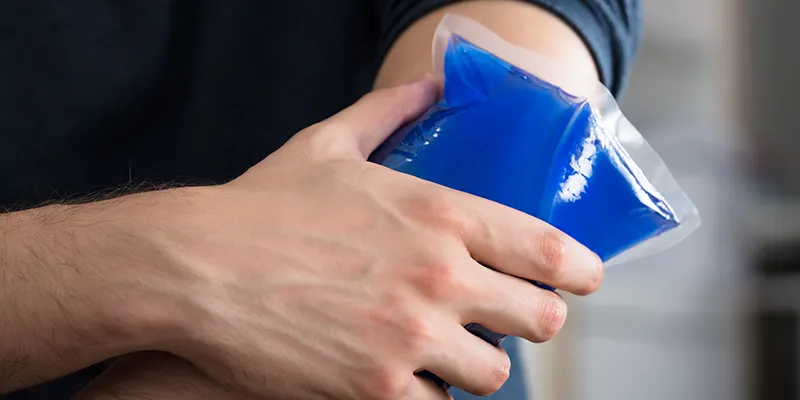
- Ice therapy: Applying ice to the affected area helps reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Cold packs or ice wrapped in a cloth can be applied for about 15–20 minutes several times a day, especially after activities.

- Pain medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, it’s essential to follow medical recommendations when using them.
- Bracing and supports: Wearing a brace or forearm strap just below the elbow can provide support, alleviate strain on the tendons and help reduce symptoms, especially during activities that may worsen tennis elbow.
- Physical therapy: A structured physical therapy program is often recommended. Therapists can guide individuals through exercises to strengthen forearm muscles, improve flexibility and correct any contributing factors like improper technique.
- Ultrasound therapy: Ultrasound treatment involves the use of sound waves to stimulate healing and reduce pain. It’s a non-invasive procedure often administered by physical therapists.
- Corticosteroid injections: In more severe cases, healthcare professionals may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and provide short-term relief. However, repeated use of these injections can have side effects.
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT): ESWT involves the application of shock waves to the affected area. This non-invasive procedure may stimulate healing and is considered for chronic cases that haven’t responded to other treatments.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: PRP therapy involves injecting a concentrated form of the patient’s own blood into the affected area to promote healing. This approach is still under research, and its effectiveness is not yet conclusively established.
- Surgery (in rare cases): Surgical intervention is considered for persistent and severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments. The procedure may involve removing damaged tissue or repairing the affected tendons.
Remedial massage for tennis elbow
Remedial massage involves the application of targeted therapeutic techniques to alleviate pain and promote healing. Skilled massage therapists focus on the affected forearm muscles, using deep tissue massage and friction therapy to stimulate blood circulation, reduce muscle tension and enhance flexibility. This personalised approach can aid in breaking down adhesions, facilitating the body’s natural healing processes.
Remedial massage is often integrated into a holistic treatment plan, complementing other interventions such as physical therapy and lifestyle modifications. Regular sessions can contribute to an improved range of motion, decreased pain and an overall enhanced sense of well-being for individuals grappling with the challenges of tennis elbow.
Preventive measures
- Proper technique: Whether you’re playing sports or performing everyday activities, using the right techniques can prevent undue stress on your forearm muscles. This includes employing the appropriate form and posture to minimise strain.
- Ergonomic adjustments: Ensure your workstation is ergonomic to minimise strain during repetitive tasks. Arrange furniture and equipment in a way that supports your natural body movements, promoting comfort and minimising muscle stress.
- Regular breaks: Incorporate regular breaks into activities involving repetitive motions. These breaks allow your muscles to rest and recover, preventing overuse injuries. Simple stretches and movements during breaks can further alleviate tension.
When to seek professional help
When your symptoms persist despite attempting home remedies or if you experience a sudden escalation in pain and swelling, seeking professional medical assistance is imperative. A healthcare professional can conduct a comprehensive evaluation, diagnose underlying issues and recommend an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your condition. Early intervention can prevent the worsening of your symptoms and promote effective recovery.

Restore the ease of pain-free movement
Tennis elbow can be a challenging condition, but with the right approach to treatment and prevention, you can find relief and regain functionality. It’s essential to listen to your body, make ergonomic adjustments and seek professional guidance for a comprehensive and effective management plan.
Always remember, early intervention and a proactive approach to care can make a significant difference in your recovery process. If you suspect tennis elbow or are experiencing persistent elbow pain, consult with a healthcare provider for personalised advice and treatment options.

